Vaccination (in 1796)
In 1796, Edward Jenner (England) tested the vaccination method to tame smallpox virus. Since then, vaccines have been widely used and very effective. Smallpox, which killed many lives during the 17th and 18th centuries, was completely eliminated with vaccines.
Many other vaccines were then developed against dangerous diseases around the world, including smallpox, rabies, tuberculosis and cholera. Today vaccines are considered an important invention of mankind, helping prevent many infectious and non-communicable diseases.
Anesthetic agents (1846)
Since BC, people have conducted many experiments on anesthetics. In 1846, Dr. William TG Morton (USA) successfully used the anesthetic ether in surgery, opening a new page for medical history.. Shortly thereafter, chloroform, a faster anesthetic, was widely used.. However, chloroform carries many risks for patients, and some deaths should be banned.
Over 150 years have passed, safer anesthetics have been developed, helping patients to reduce pain during surgery.
Pathogen theory (1861)
Before the germ theory was introduced, many believed that the origin of disease was "spontaneous" . In other words, ancient doctors thought that illness could appear in the air itself, instead of spreading through the air or being spread through direct skin contact.
In 1861, by a simple experiment, French bacteriologist Louis Pasteur proved that the origin of infectious disease was that germs attacked people. This discovery marks an important milestone in medical history, changing the way to treat, control and prevent disease, prevent epidemics from taking thousands of lives every year such as plague, dysentery and typhoid fever. .
Medical photo (1895)
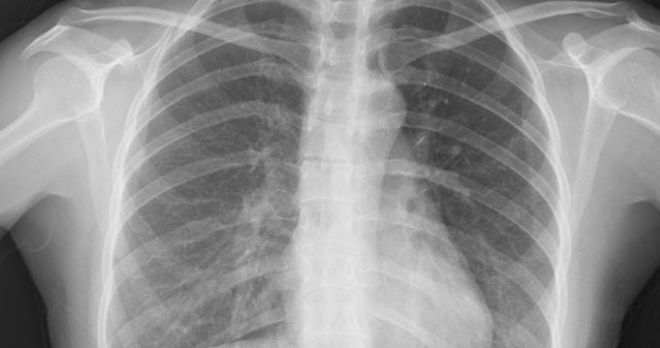
X-ray is the first medical imaging diagnostic technique in history. In 1895, German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Rӧntgen discovered this technique when he was experimenting with electricity through cathode ray tubes. Just overnight, his discovery completely changed the medical industry. In 1896, Glasgow Hospital opened the world's first radiology department.
Ultrasound has been in the diagnostic imaging department since 1955. Doctors use high-frequency sound waves to create technical images, to support diagnosis.
In 1967, computerized tomography (CT) technology was invented, using X-rays and computers to diagnose many different diseases. CT scanners have become an important diagnostic tool in modern medicine.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology was invented in 1973 by Paul Lauterbur. Nuclear magnetic resonance data produces detailed images of the body, detecting tumors, cysts, brain and spinal cord injury and a number of heart and liver problems.
Penicillin (1928)